3.1How I envision the
impact on the future of business and society. A post in the title of ‘The
Internet of Things’.
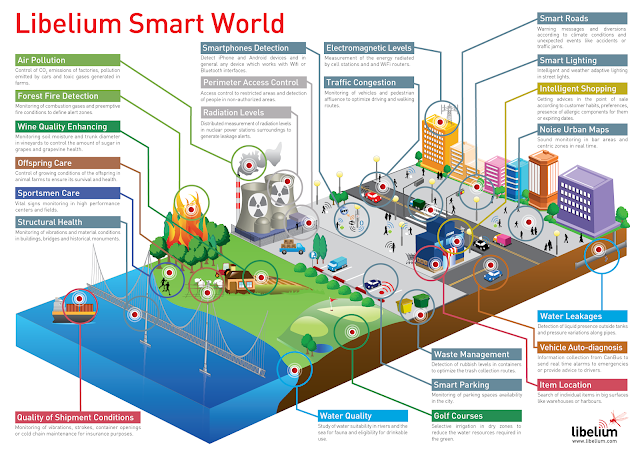
The term Internet of Things generally refers
to scenarios where network connectivity
and computing capability extends to objects, sensors and everyday items not
normally considered computers, allowing these devices to generate, exchange and
consume data with minimal human intervention.
 The Internet of Things has the potential to
really shift the way we do things, think
and learn (Module Manual, 2016, p.77).
Is a system of
interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects,
animals or people that are provided with unique identities and the ability to
transfer data over a network in one form or the another, receiving and processing
information in real time and creating new ways of making decisions back-up
by the availability of information.
The Internet of Things has the potential to
really shift the way we do things, think
and learn (Module Manual, 2016, p.77).
Is a system of
interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects,
animals or people that are provided with unique identities and the ability to
transfer data over a network in one form or the another, receiving and processing
information in real time and creating new ways of making decisions back-up
by the availability of information.
Internet
of Things will affect future businesses in core areas such as
production, advertising, sale, market research, and job market and enterprise
resource management. Most of the advantages are not user targeted but with the
introduction of Internet of Things, massive volume of information
about the consumer lifestyle and interests can be collected. This
data reveals that the hidden buying patterns of each user which provide the
insight to advertisers to advertise to each and every consumer.
When coming to market
research, all smart household devices are equipped with sensors, which will do
the market research free of charge for the businesses. Internet of Things
products will not only generate revenue for businesses but also provide insight
to consumers after the sales. Internet of Things will also have an impact on
the hiring processes.
This overview document
is designed to help the Internet Society community to navigate the dialogue
surrounding the Internet of Things in light of the competing predictions about
its promises and perils. The Internet of Things engages a broad set of ideas that are complex and intertwined from different
perspectives.
3.2Any four (4) of
several aspects of intelligence and their explanation of the importance of
these levels with regard to the business context to and the impact of
technology.
Spatial
Intelligence “Picture Smart”
This is the ability to recognize, use and interpret
images and patterns and to reproduce objects in three (3) dimensions namely; successful
architects, sculptors and designers are likely to have high spatial
intelligence.
Basically, spatial intelligence is the ability to
think in three dimensions. Core capacities include mental imagery, spatial reasoning, image manipulation, graphic and
artistic skills, and an active imagination. Young adults with this kind of
intelligence may be fascinated with spend free time drawing or daydreaming.
Interpersonal
Intelligence “People Smart”
This is the ability to understand people's intentions,
motivations and desires. This intelligence allows individuals to work well with others.
Professions like therapy, teaching and sales attract individuals with high
interpersonal intelligence.
Interpersonal intelligence is the ability to
understand and interact effectively with others. It involves effective verbal and nonverbal
communication, the ability to note distinctions among others, sensitivity to
the moods and temperaments of others, and the ability to entertain multiple
perspectives.
Teachers, social workers, actors, and politicians all
exhibit interpersonal intelligence. Young adults with this kind of intelligence
are leaders among their peers, are good at communicating, and seem to
understand others’ feelings and motives.
Linguistic
Intelligence “Word Smart”
Linguistic intelligence is the ability to think in words and to use language to
express and appreciate complex meanings.
It allows us to understand the order and meaning of words and to apply
meta-linguistic skills to reflect on our use of language.
Linguistic intelligence is the most widely shared human competence and is evident in poets,
novelists, journalists, and effective public speakers. Young adults with
this kind of intelligence enjoy writing,
reading, telling stories or doing crossword puzzles. (Stated by Howard Gardner)
Logical-Mathematical
Intelligence “Number/Reasoning Smart”
According to Howard
Gardner it was stated that; Logical-mathematical intelligence is
the ability to calculate, quantify,
consider propositions and hypotheses, and carry out complete mathematical
operations. It enables us to perceive relationships and connections and to
use abstract, symbolic thought; sequential reasoning skills; and inductive and
deductive thinking patterns.
Logical intelligence is usually well developed in
mathematicians, scientists, and detectives. Young adults with lots of logical intelligence
are interested in patterns, categories,
and relationships. They are drawn to arithmetic problems, strategy games and
experiments.


No comments:
Post a Comment